- Joined
- May 15, 2016
- Messages
- 14,528
- Likes
- 2,645
- Points
- 1,730
Group-IB experts released a report on Hi-Tech Crime Trends 2019-2020 , dedicated to attacks on various industries and critical infrastructure, as well as campaigns aimed at destabilizing the Internet in individual countries.
The authors of the report examined the activity of the most dangerous cybercriminal groups, as well as pro-state attackers, whose goal is espionage and sabotage. In total, 38 groups sponsored by the states were active during the study period, 7 of which were new.
The report was already the sixth Hi-Tech Crime Trends and this year it was first divided into the main attacked industries and traditionally covers the period H2 2018 - H1 2019 compared to H2 2017 - H1 2018.
“The past three years have clearly shown the speed of escalation of threats in cyberspace, if 2017 was the year of the epidemic of the cryptographic viruses WannaCry, NotPetya and BadRabbit, then 2018 revealed a weak readiness for side-channel attacks and threats related to vulnerabilities in microprocessors. But 2019 was the year of open military cyber operations. The conflict between states has taken on new forms, and cyber activity plays a leading role in this confrontation. The focus of researchers around the world is gradually shifting from financially-motivated hacker groups making money by hacking various organizations towards pro-government attackers. Their activity goes unnoticed for years, few precedents become public, but most of them indicate that critical infrastructure facilities in many countries are already compromised. This suggests that a peaceful existence is no longer possible in isolation from cybersecurity: no state, no corporation, no people can ignore this factor, ”says Dmitry Volkov, technical director, head of Threat Intelligence, co-founder of Group-IB.
Espionage and sabotage
According to researchers, this year cybersecurity has come to the fore on the global political agenda. Blackout in Venezuela, open military operations in cyberspace between conflicting states, as well as disruption of the Internet in individual countries, are extremely dangerous precedents that can lead to social and economic damage, as well as destabilizing the situation in states.

During the second half of 2018 and the first half of 2019, cybersecurity experts discovered a large number of previously unknown state-sponsored groups. One of the groups was disclosed by Group-IB at the end of 2019, it received the name RedCurl. Its goals are insurance, consulting and construction companies in different countries of the world, including Russia. RedCurl is distinguished by the quality of targeted phishing attacks and the use of legitimate services, which greatly complicates its detection in the company's infrastructure.
Many APT groups analyzed in the report have been conducting their operations for several years, but for a long time they went unnoticed. Some of them attack similar targets, which leads to competition between them and faster detection of their actions. One of the trends in the active confrontation of attackers has been the use of Hacking back, when the attackers themselves become victims. This trick is prohibited for use by private companies.
Internet destabilization
Unrealistic scenarios of disconnecting the country from the Internet are becoming more likely, the researchers write. To carry out an attack that could violate the stability of the global network in a particular country, long preparations are required, however, the attacks analyzed in the Group-IB report prove that it is technically possible.
Domain name registrars are part of the country's critical infrastructure. Since disruption of their work affects the functioning of the global network, they are the object of attacks from pro-government attackers. As the past months have shown, the most dangerous are Hijacking DNS hacks, as a result of which attackers could manage DNS records for MITM attacks, as well as traffic manipulations and Hijacking BGP attacks during which the route is intercepted and the traffic of individual autonomous system prefixes is redirected through third-party equipment. The main ways to use BGP Hijacking are espionage and disruption of the work of large telecom operators.
Telecommunications sector
Group-IB identifies 9 groups (APT10, APT33, MuddyWater, HEXANE, Thrip, Chafer, Winnti, Regin and Lazarus), which posed a threat to the telecommunications sector during this period. The outgoing year has shown that the telecom industry is one of the priority for pro-government groups: having compromised the operator, attackers get the opportunity to develop attacks in his clients with the aim of espionage or sabotage. The new driver of threats in this industry is the spread of 5G technology. In fact, all threats to server and software solutions become relevant for 5G operators. Among them: BIOS / UEFI-related attacks, side channel and supply chain. Also, due to the large number of connected devices and wide bandwidth, the power and frequency of DDoS attacks will significantly increase. Energy sector

The seven groups described in the report (LeafMiner, BlackEnergy, Dragonfly, HEXANE, Xenotime, APT33 and Lazarus) specialize mainly in espionage, and in some cases, the failure of infrastructure or individual systems of energy facilities in different countries.
So, in 2019, the Lazarus group attacked an energy nuclear corporation in India, which led to the shutdown of the second power unit. The atypical choice of the victim allows us to conclude that the military departments of unfriendly countries are interested in such attacks. Since Stuxnet, the Middle East has been the main testing ground for instruments. The vector of penetration into isolated segments of the OT network is the compromise of the IT network using malware and techniques, including Living off the land.

With the exception of the above example, the tools of these groups remain hidden. In recent years, only two frameworks have been identified that are capable of influencing technological processes - Industroyer and Triton (Trisis). Both of them were disclosed as a result of the mistakes of the attackers, which allows us to conclude that there are much more carefully masked and not yet detected threats. Among the attacks specific to the energy industry, experts identify supply chains - attacks through suppliers of software and hardware. First of all, management companies will be compromised, and through them will develop an attack on energy facilities.
Banking sector: Russian-speaking hackers switched to international goals
Hacking banks around the world is the prerogative of Russian-speaking hackers: they still make up the majority of attacking groups. In 2018, a new band SilentCards from Kenya was added to the “Russian-speaking troika” - Cobalt, Silence and MoneyTaker, as well as North Korean Lazarus.
As before, only Cobalt, Silence and MoneyTaker have Trojans that allow you to manage an ATM dispenser and withdraw money. At the same time, for the study period, only Silence hackers attacked through ATMs, Silence and SilentCards through card processing, and Lazarus through SWIFT (2 successful thefts: in the total amount of $ 16 million in India and Malta).

Only the North Korean APT group uses the FastCash theft method. Behind all attacks of this type is the Lazarus group. Silence reduced activity on its own phishing mailings and began to gain access to target banks from other hacker groups, in particular, from TA505. At the moment, SilentCards is the least technically prepared among these groups and so far has successfully targeted only banks in Africa.
Using the Russian market as a testing ground, the “Russian-speaking troika” continues its geographic expansion. Since July last year, targets were attacked three times in India (Silence, Lazarus), in Vietnam (Lazarus), in Pakistan (Lazarus), in Malta (Lazarus), in Thailand (Lazarus), in Chile (Lazarus, Silence), during Vietnam (Lazarus), Kenya (SilentCards), Russia (MoneyTaker, Cobalt, Silence), Bulgaria (Cobalt, Silence), as well as one attack, Silence carried out in Costa Rica, Ghana and Bangladesh.
To withdraw money, these groups will continue to use attacks on the card processing system and Trojans for ATMs. SWIFT will be much less likely to fall into the focus of these groups. Lazarus will remain the only group to commit theft through SWIFT and ATM Switch. Successful attacks on banks will culminate in the disabling of infrastructure to hide traces. Supposedly, SilentCards will remain a local group and will attack banks in Africa. Most likely, it will expand the list of targets at the expense of other industries, where the main vector will be extortion through the use of encryption programs.
In Russia, the market for high-tech crime in the financial sector fell by 85%
At the same time, researchers note that the reduction in Russia of damage from all types of cybercrime with the use of malvari aimed directly at banks and their customers led to a record drop in the market by 85%.
According to analysts, the high-tech crime market in the financial industry in Russia fell to 510 million rubles for the period H2 2018 - H1 2019 against 3.2 billion rubles in the previous period. Against the background of the exodus of financially motivated groups from the RU zone, the reduction in the number of Android Trojans and phishing groups, the number of crimes against bank customers using social engineering and telephone fraud is growing in Russia.
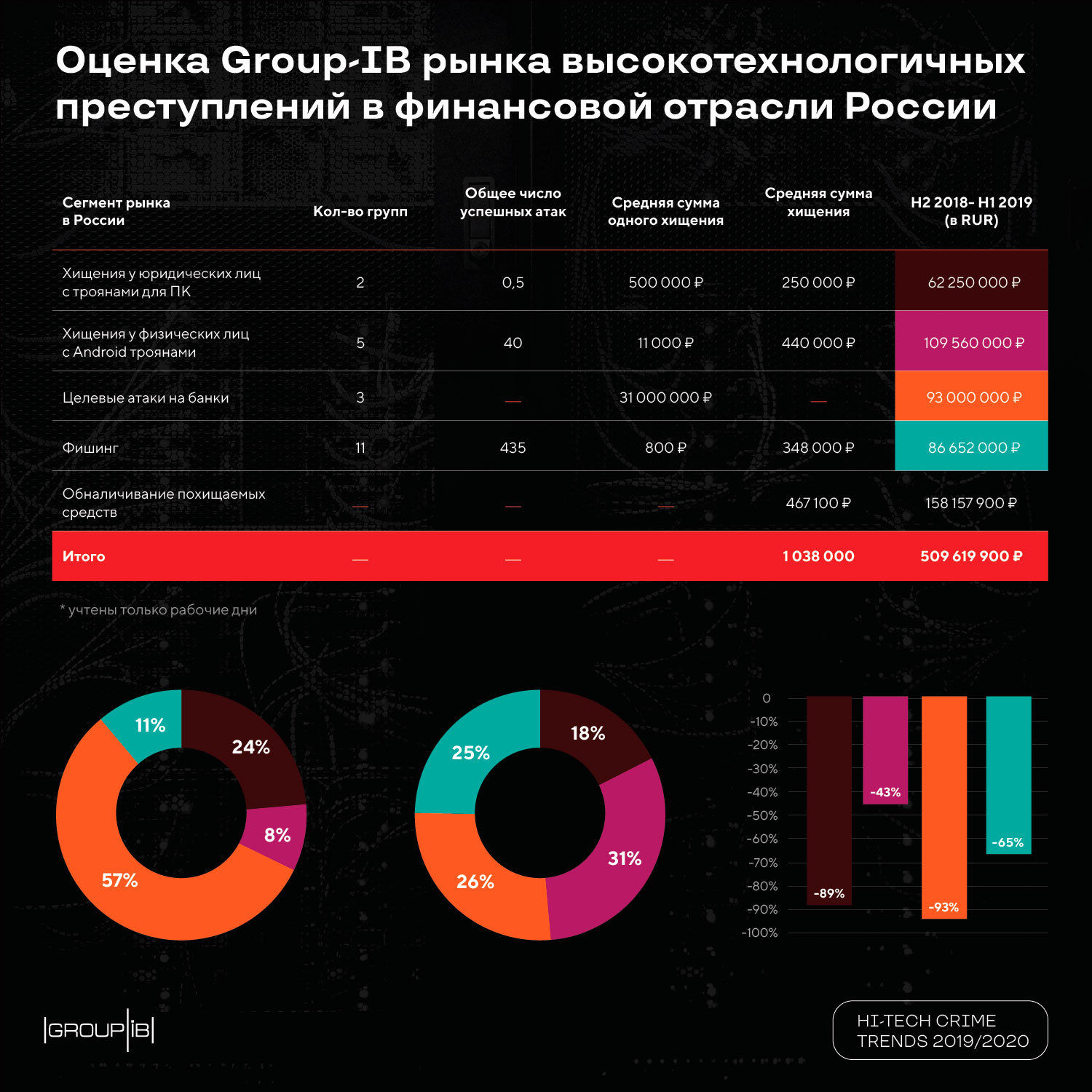
As mentioned above, experts identify 5 groups that successfully carry out targeted attacks on banks and pose a real threat to the financial sector in the world. Among them are the “Russian-speaking troika” - Cobalt, Silence and MoneyTaker, as well as North Korean Lazarus (North Korea) and the new SilentCards from Kenya.
With respect to Russian banks, Cobalt and Silence carried out one successful attack for the study period, MoneyTaker - two. The first two Russian-speaking groups shifted their focus to foreign goals, which led to a multiple reduction of damage “according to RU”. According to the report, to 93 million rubles, that is, losses from targeted attacks on banks in Russia by financially motivated groups decreased by almost 14 times. Compared with the previous period, the average amount of theft from targeted attacks on banks in Russia fell from 118 to 31 million rubles.
According to Group-IB forecasts, the Russian-speaking troika will continue its geographic expansion outside the RU. To withdraw money, they will use attacks on the card processing system and trojans for ATMs. SWIFT will be much less likely to fall into the focus of these groups. Lazarus will remain the only group to commit theft through SWIFT and ATM Switch. Successful attacks on banks will culminate in the disabling of infrastructure to hide traces. Supposedly, SilentCards will remain a local group attacking banks in its region.
The triumph of social engineering
According to the theft with the help of Trojans for PCs, whose “homeland” has always been Russia, the damage was reduced by 89% and amounted to 62 million rubles. Russian-speaking hackers stopped creating new desktop trojans. There are only two groups left that steal money in Russia using Trojans for PCs - Buhtrap2 and RTM. Only the latter is active.
Trojans for Android devices disappear more slowly, but theft with this type of malvari is also on the decline: the damage in this segment amounted to 110 million rubles, which is 43% lower than in the previous period.
The number of groups using Android trojans in Russia decreased from 8 to 5: at the same time, the “heavyweights” left - the Trojans that account for the largest number of fraudulent transactions. The remaining groups refused the SMS-channel for theft, it was replaced by the card2card transfer method, which led to an increase in the average size of the theft from 7 to 11 thousand rubles. In general, over the past period, 22 trojans have become obsolete; in total, only 7 new ones have been created.
The damage from financial phishing in Russia fell by 65% to the level of 87 million rubles. The overall figure was affected by both a reduction in the number of active groups and a decrease in the “average check” of an attack. The decrease in financial gain led to the exit of the game 15 groups that earned on phishing attacks. 11 remained active.
All this forces scammers to look for new ways to earn money using bank card data. As a result, fraud using social engineering techniques came out on top in terms of the extent of the threat spread in Russia. First of all, we are talking about telephone fraud - vishing, which since the end of 2018 has literally swept the banking market. Behavioral analysis of user sessions to identify suspicious activity in remote banking systems is still the prerogative of large banks. Therefore, in Russia it is precisely this type of attack on bank customers that will retain high momentum.
Carding on the rise
The volume of the carding market for the study period increased by 33% and amounted to more than 56 billion rubles. ($ 879,680,072). The number of compromised cards posted on underground forums increased 38% from 27.1 to 43.8 million compared to the previous period.
Dumps (contents of magnetic strips of cards) make up 80% of the carding market. Over the study period, 31.2 million dumps were found for sale, which is 46% higher than last year. Selling text data (number, CVV, validity period) is also on the rise: their growth was 19%.
The average price for text data rose from $ 9 to $ 14, while the average price of the dump decreased from $ 33 to $ 22.
The lowest price is usually set for compromised data of American banks, they, on average, go for $ 8-10 for fresh text card data and $ 16-24 for dumps. Traditionally, a high price on European bank cards: $ 18-21 for a text, $ 100-120 for a dump. Russian cards remain rare in large card shops, most of which do not work “according to RU”.
Cards of Russian banks are usually in the average price range, and from the last period the average price for a dump has increased significantly - from $ 48 to $ 71 (4,500 rubles) and the price for a text has slightly decreased from $ 15 to $ 12 (760 rubles). At the same time, the maximum price for a dump card of a Russian bank in 2018 reached $ 170 (10,000 rubles), and in 2019 rose to the mark of $ 500 (32,000 rubles).
The new trend working to increase the volume of textual data of bank cards on sale is JS-sniffers. This year, Group-IB experts have identified at least 38 different families of JS-sniffers, their number is growing and already exceeds the number of banking Trojans. In terms of compromise with the help of JS-sniffers, the United States occupies the first position and the United Kingdom the second. This threat will be relevant primarily for countries where 3D Secure is not common.
Phishing remains a “long-playing” method for obtaining textual data about bank cards of users. Competition in this segment is growing: attackers began to use panels to control web injects and auto-loading, which used to be the prerogative of banking Trojans. The developers of phishing whales began to pay more attention.
The authors of the report examined the activity of the most dangerous cybercriminal groups, as well as pro-state attackers, whose goal is espionage and sabotage. In total, 38 groups sponsored by the states were active during the study period, 7 of which were new.
The report was already the sixth Hi-Tech Crime Trends and this year it was first divided into the main attacked industries and traditionally covers the period H2 2018 - H1 2019 compared to H2 2017 - H1 2018.
“The past three years have clearly shown the speed of escalation of threats in cyberspace, if 2017 was the year of the epidemic of the cryptographic viruses WannaCry, NotPetya and BadRabbit, then 2018 revealed a weak readiness for side-channel attacks and threats related to vulnerabilities in microprocessors. But 2019 was the year of open military cyber operations. The conflict between states has taken on new forms, and cyber activity plays a leading role in this confrontation. The focus of researchers around the world is gradually shifting from financially-motivated hacker groups making money by hacking various organizations towards pro-government attackers. Their activity goes unnoticed for years, few precedents become public, but most of them indicate that critical infrastructure facilities in many countries are already compromised. This suggests that a peaceful existence is no longer possible in isolation from cybersecurity: no state, no corporation, no people can ignore this factor, ”says Dmitry Volkov, technical director, head of Threat Intelligence, co-founder of Group-IB.
Espionage and sabotage
According to researchers, this year cybersecurity has come to the fore on the global political agenda. Blackout in Venezuela, open military operations in cyberspace between conflicting states, as well as disruption of the Internet in individual countries, are extremely dangerous precedents that can lead to social and economic damage, as well as destabilizing the situation in states.

During the second half of 2018 and the first half of 2019, cybersecurity experts discovered a large number of previously unknown state-sponsored groups. One of the groups was disclosed by Group-IB at the end of 2019, it received the name RedCurl. Its goals are insurance, consulting and construction companies in different countries of the world, including Russia. RedCurl is distinguished by the quality of targeted phishing attacks and the use of legitimate services, which greatly complicates its detection in the company's infrastructure.
Many APT groups analyzed in the report have been conducting their operations for several years, but for a long time they went unnoticed. Some of them attack similar targets, which leads to competition between them and faster detection of their actions. One of the trends in the active confrontation of attackers has been the use of Hacking back, when the attackers themselves become victims. This trick is prohibited for use by private companies.
Internet destabilization
Unrealistic scenarios of disconnecting the country from the Internet are becoming more likely, the researchers write. To carry out an attack that could violate the stability of the global network in a particular country, long preparations are required, however, the attacks analyzed in the Group-IB report prove that it is technically possible.
Domain name registrars are part of the country's critical infrastructure. Since disruption of their work affects the functioning of the global network, they are the object of attacks from pro-government attackers. As the past months have shown, the most dangerous are Hijacking DNS hacks, as a result of which attackers could manage DNS records for MITM attacks, as well as traffic manipulations and Hijacking BGP attacks during which the route is intercepted and the traffic of individual autonomous system prefixes is redirected through third-party equipment. The main ways to use BGP Hijacking are espionage and disruption of the work of large telecom operators.
Telecommunications sector
Group-IB identifies 9 groups (APT10, APT33, MuddyWater, HEXANE, Thrip, Chafer, Winnti, Regin and Lazarus), which posed a threat to the telecommunications sector during this period. The outgoing year has shown that the telecom industry is one of the priority for pro-government groups: having compromised the operator, attackers get the opportunity to develop attacks in his clients with the aim of espionage or sabotage. The new driver of threats in this industry is the spread of 5G technology. In fact, all threats to server and software solutions become relevant for 5G operators. Among them: BIOS / UEFI-related attacks, side channel and supply chain. Also, due to the large number of connected devices and wide bandwidth, the power and frequency of DDoS attacks will significantly increase. Energy sector

The seven groups described in the report (LeafMiner, BlackEnergy, Dragonfly, HEXANE, Xenotime, APT33 and Lazarus) specialize mainly in espionage, and in some cases, the failure of infrastructure or individual systems of energy facilities in different countries.
So, in 2019, the Lazarus group attacked an energy nuclear corporation in India, which led to the shutdown of the second power unit. The atypical choice of the victim allows us to conclude that the military departments of unfriendly countries are interested in such attacks. Since Stuxnet, the Middle East has been the main testing ground for instruments. The vector of penetration into isolated segments of the OT network is the compromise of the IT network using malware and techniques, including Living off the land.

With the exception of the above example, the tools of these groups remain hidden. In recent years, only two frameworks have been identified that are capable of influencing technological processes - Industroyer and Triton (Trisis). Both of them were disclosed as a result of the mistakes of the attackers, which allows us to conclude that there are much more carefully masked and not yet detected threats. Among the attacks specific to the energy industry, experts identify supply chains - attacks through suppliers of software and hardware. First of all, management companies will be compromised, and through them will develop an attack on energy facilities.
Banking sector: Russian-speaking hackers switched to international goals
Hacking banks around the world is the prerogative of Russian-speaking hackers: they still make up the majority of attacking groups. In 2018, a new band SilentCards from Kenya was added to the “Russian-speaking troika” - Cobalt, Silence and MoneyTaker, as well as North Korean Lazarus.
As before, only Cobalt, Silence and MoneyTaker have Trojans that allow you to manage an ATM dispenser and withdraw money. At the same time, for the study period, only Silence hackers attacked through ATMs, Silence and SilentCards through card processing, and Lazarus through SWIFT (2 successful thefts: in the total amount of $ 16 million in India and Malta).

Only the North Korean APT group uses the FastCash theft method. Behind all attacks of this type is the Lazarus group. Silence reduced activity on its own phishing mailings and began to gain access to target banks from other hacker groups, in particular, from TA505. At the moment, SilentCards is the least technically prepared among these groups and so far has successfully targeted only banks in Africa.
Using the Russian market as a testing ground, the “Russian-speaking troika” continues its geographic expansion. Since July last year, targets were attacked three times in India (Silence, Lazarus), in Vietnam (Lazarus), in Pakistan (Lazarus), in Malta (Lazarus), in Thailand (Lazarus), in Chile (Lazarus, Silence), during Vietnam (Lazarus), Kenya (SilentCards), Russia (MoneyTaker, Cobalt, Silence), Bulgaria (Cobalt, Silence), as well as one attack, Silence carried out in Costa Rica, Ghana and Bangladesh.
To withdraw money, these groups will continue to use attacks on the card processing system and Trojans for ATMs. SWIFT will be much less likely to fall into the focus of these groups. Lazarus will remain the only group to commit theft through SWIFT and ATM Switch. Successful attacks on banks will culminate in the disabling of infrastructure to hide traces. Supposedly, SilentCards will remain a local group and will attack banks in Africa. Most likely, it will expand the list of targets at the expense of other industries, where the main vector will be extortion through the use of encryption programs.
In Russia, the market for high-tech crime in the financial sector fell by 85%
At the same time, researchers note that the reduction in Russia of damage from all types of cybercrime with the use of malvari aimed directly at banks and their customers led to a record drop in the market by 85%.
According to analysts, the high-tech crime market in the financial industry in Russia fell to 510 million rubles for the period H2 2018 - H1 2019 against 3.2 billion rubles in the previous period. Against the background of the exodus of financially motivated groups from the RU zone, the reduction in the number of Android Trojans and phishing groups, the number of crimes against bank customers using social engineering and telephone fraud is growing in Russia.

As mentioned above, experts identify 5 groups that successfully carry out targeted attacks on banks and pose a real threat to the financial sector in the world. Among them are the “Russian-speaking troika” - Cobalt, Silence and MoneyTaker, as well as North Korean Lazarus (North Korea) and the new SilentCards from Kenya.
With respect to Russian banks, Cobalt and Silence carried out one successful attack for the study period, MoneyTaker - two. The first two Russian-speaking groups shifted their focus to foreign goals, which led to a multiple reduction of damage “according to RU”. According to the report, to 93 million rubles, that is, losses from targeted attacks on banks in Russia by financially motivated groups decreased by almost 14 times. Compared with the previous period, the average amount of theft from targeted attacks on banks in Russia fell from 118 to 31 million rubles.
According to Group-IB forecasts, the Russian-speaking troika will continue its geographic expansion outside the RU. To withdraw money, they will use attacks on the card processing system and trojans for ATMs. SWIFT will be much less likely to fall into the focus of these groups. Lazarus will remain the only group to commit theft through SWIFT and ATM Switch. Successful attacks on banks will culminate in the disabling of infrastructure to hide traces. Supposedly, SilentCards will remain a local group attacking banks in its region.
The triumph of social engineering
According to the theft with the help of Trojans for PCs, whose “homeland” has always been Russia, the damage was reduced by 89% and amounted to 62 million rubles. Russian-speaking hackers stopped creating new desktop trojans. There are only two groups left that steal money in Russia using Trojans for PCs - Buhtrap2 and RTM. Only the latter is active.
Trojans for Android devices disappear more slowly, but theft with this type of malvari is also on the decline: the damage in this segment amounted to 110 million rubles, which is 43% lower than in the previous period.
The number of groups using Android trojans in Russia decreased from 8 to 5: at the same time, the “heavyweights” left - the Trojans that account for the largest number of fraudulent transactions. The remaining groups refused the SMS-channel for theft, it was replaced by the card2card transfer method, which led to an increase in the average size of the theft from 7 to 11 thousand rubles. In general, over the past period, 22 trojans have become obsolete; in total, only 7 new ones have been created.
The damage from financial phishing in Russia fell by 65% to the level of 87 million rubles. The overall figure was affected by both a reduction in the number of active groups and a decrease in the “average check” of an attack. The decrease in financial gain led to the exit of the game 15 groups that earned on phishing attacks. 11 remained active.
All this forces scammers to look for new ways to earn money using bank card data. As a result, fraud using social engineering techniques came out on top in terms of the extent of the threat spread in Russia. First of all, we are talking about telephone fraud - vishing, which since the end of 2018 has literally swept the banking market. Behavioral analysis of user sessions to identify suspicious activity in remote banking systems is still the prerogative of large banks. Therefore, in Russia it is precisely this type of attack on bank customers that will retain high momentum.
Carding on the rise
The volume of the carding market for the study period increased by 33% and amounted to more than 56 billion rubles. ($ 879,680,072). The number of compromised cards posted on underground forums increased 38% from 27.1 to 43.8 million compared to the previous period.
Dumps (contents of magnetic strips of cards) make up 80% of the carding market. Over the study period, 31.2 million dumps were found for sale, which is 46% higher than last year. Selling text data (number, CVV, validity period) is also on the rise: their growth was 19%.
The average price for text data rose from $ 9 to $ 14, while the average price of the dump decreased from $ 33 to $ 22.
The lowest price is usually set for compromised data of American banks, they, on average, go for $ 8-10 for fresh text card data and $ 16-24 for dumps. Traditionally, a high price on European bank cards: $ 18-21 for a text, $ 100-120 for a dump. Russian cards remain rare in large card shops, most of which do not work “according to RU”.
Cards of Russian banks are usually in the average price range, and from the last period the average price for a dump has increased significantly - from $ 48 to $ 71 (4,500 rubles) and the price for a text has slightly decreased from $ 15 to $ 12 (760 rubles). At the same time, the maximum price for a dump card of a Russian bank in 2018 reached $ 170 (10,000 rubles), and in 2019 rose to the mark of $ 500 (32,000 rubles).
The new trend working to increase the volume of textual data of bank cards on sale is JS-sniffers. This year, Group-IB experts have identified at least 38 different families of JS-sniffers, their number is growing and already exceeds the number of banking Trojans. In terms of compromise with the help of JS-sniffers, the United States occupies the first position and the United Kingdom the second. This threat will be relevant primarily for countries where 3D Secure is not common.
Phishing remains a “long-playing” method for obtaining textual data about bank cards of users. Competition in this segment is growing: attackers began to use panels to control web injects and auto-loading, which used to be the prerogative of banking Trojans. The developers of phishing whales began to pay more attention.








